产品中心
联系我们
销售专用:
地址:北京市海淀区西小口路66号中关村东升科技园C-1楼三层

- 产品描述
- 参考文献
-
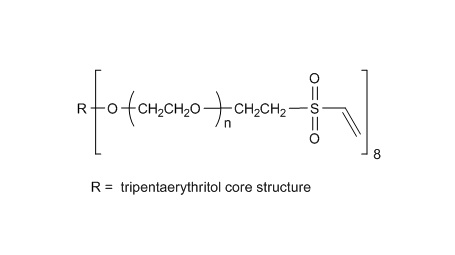
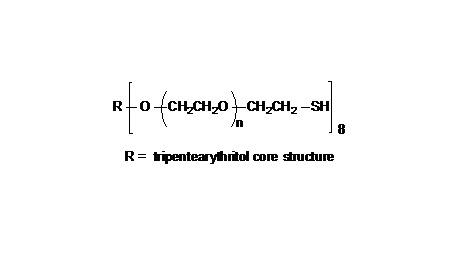
键凯科技提供高品质八臂聚乙二醇巯基产品,取代率≥ 95%。
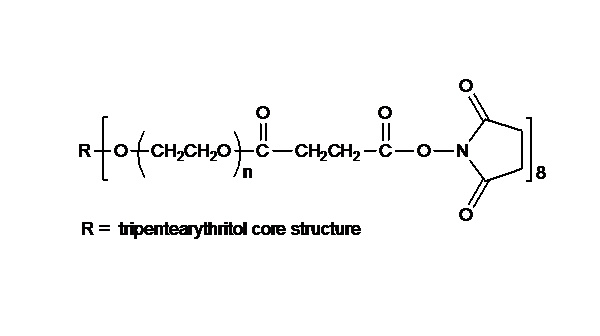
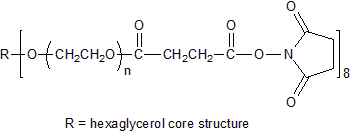
键凯科技的8臂巯基产品可交联制备PEG水凝胶产品。PEG水凝胶在医疗器械和再生医学方面尤其是在药物的缓释控释,2维和3维细胞培养以及伤口的缝合和愈合方面有非常广泛的应用。键凯的8臂PEG原料来通过三聚季戊四醇和乙氧基聚合而成,每个PEG链的乙氧基单元数目不是完全相同的。键凯的多臂PEG产品的分子量指的是各臂分子量的总和。
键凯科技提供8ARM-SH分子量 10000Da, 20000 Da产品 1克和10克包装。
键凯科技提供分装服务,需要收取分装费用,如果您需要分装为其他规格请与我们联系。
键凯科技同时提供其他分子量的8ARM-SH产品,如你需要请与我司[email protected]联系。
键凯科技提供大批量生产产品及GMP级别产品,如需报价请与我们联系。
-
References:
1. Rao, V.V., et al., Rescuing mesenchymal stem cell regenerative properties on hydrogel substrates post serial expansion, Bioengineering & translational medicine, 2019.
2. Brown, T.E., et al., Photopolymerized dynamic hydrogels with tunable viscoelastic properties through thioester exchange, Biomaterials, 2018.
3. Aziz, A.H., et al., Mechanical characterization of sequentially layered photo-clickable thiol-ene hydrogels, Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials, 2017, V. 65, p. 454-465.
4. Huynh, C.T., et al., Cytocompatible Catalyst-free Photodegradable Hydrogels for Light-Mediated RNA Release to Induce hMSC Osteogenisis. ACS Biomaterials Science & Engineering, 2017.
5. Suma, T., et al., Modulated Fragmentation of Proapoptotic Peptide Nanoparticles Regulates Cytotoxicity. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2017, 139(11):4009-18.
6. Liang, Y., et al., Controlled release of an anthrax toxin-neutralizing antibody from hydrolytically degradable polyethylene glycol hydrogels, Journal of Biomedical Materials Research Part A, 2016, V. 104:1, p. 113–123.
7. Lee, S., et al., Effects of the poly(ethylene glycol) hydrogel crosslinking mechanism on protein release, Biomater. Sci., 2016.
8. Huynh, C.T., et al., Light-triggered RNA release and induction of hMSC osteogenesis via photodegradable, dual-crosslinked hydrogels. Nanomedicine, 2016.
9. Shih, H., et al., Photo-click hydrogels prepared from functionalized cyclodextrin and poly(ethylene glycol) for drug delivery and in situ cell encapsulation, Biomacromolecules, 2015.
10. Nguyen, M.K., et al., Sustained localized presentation of RNA interfering molecules from in situ forming hydrogels to guide stem cell osteogenic differentiation. Biomaterials, 2014, 35(24), p. 6278-6286.
11. Lee, S., et al., The effects of varying poly(ethylene glycol) hydrogel crosslinking density and the crosslinking mechanism on protein accumulation in three-dimensional hydrogels, Acta Biomaterialia, 2014, 10(10), p. 4167–4174.
12.Wilson, RL, et al, Protein-functionalized poly (ethylene glycol) hydrogels as scaffolds for monolayer organoid culture. Tissue Engineering Part C: Methods. 2021, 27(1):12-23.
13.Castilho, M., et l., Hydrogel-based bioinks for cell electrowriting of well-organized living structures with micrometer-scale resolution. Biomacromolecules. 2021, 22(2):855-66.
14.McKee, C, et al., Transcriptomic analysis of naïve human embryonic stem cells cultured in three-dimensional PEG scaffolds. Biomolecules. 2021, 11(1):21.
15.Su, Q., et al., Facile preparation of a metal-phenolic network-based lymph node targeting nanovaccine for antitumor immunotherapy, Acta Biomaterialia, V. 158, 2023, P. 510-524.
16.Pham-Nguyen, O.V, et al., Complete breakdown of copper-free clickable doxorubicin nanoclusters for real-time tumor proliferation tracking, Chemical Engineering Journal, 468, 2023.
17.Wan, W., et l., TGF-β1 promotes osteogenesis of mesenchymal stem cells via integrin mediated mechanical positive autoregulation, iScience, 2024, v. 27, I7. Keywords: Mechanobiology; Biological sciences; Cell biology; Mathematical biosciences; 8-arm PEG maleimide; 8-arm PEG thiol
产品询价